First, we must consider the different neuropathic pain types. Neuropathic pain can be diverse in nature, encompassing a wide range of pain types, including post-herpetic neuralgia (PHN), painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN), and painful cancer-related neuropathies.
Gabapentin has been shown to be beneficial in treating several types of neuropathic pain; however, the mechanism of action by which gabapentin exerts its analgesic effect is still unknown.
It is suggested that gabapentin may block the calcium channel alpha(2)delta (a2d)-1 receptor in the brain. This protein-modulated receptor is involved in excitatory synapse formation. Therefore, the therapeutic effects of gabapentin may be attributed to prevention of new synapse formations.
Even with sufficient data supporting the use of gabapentin in the treatment of various neuropathic pain conditions, gabapentin only has Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for PHN. Dosing recommendations for off-label use of gabapentin can be somewhat ambiguous, if a recommendation exists at all. Therefore, several studies further investigate dosing regimens specific to other neuropathic pain syndromes.

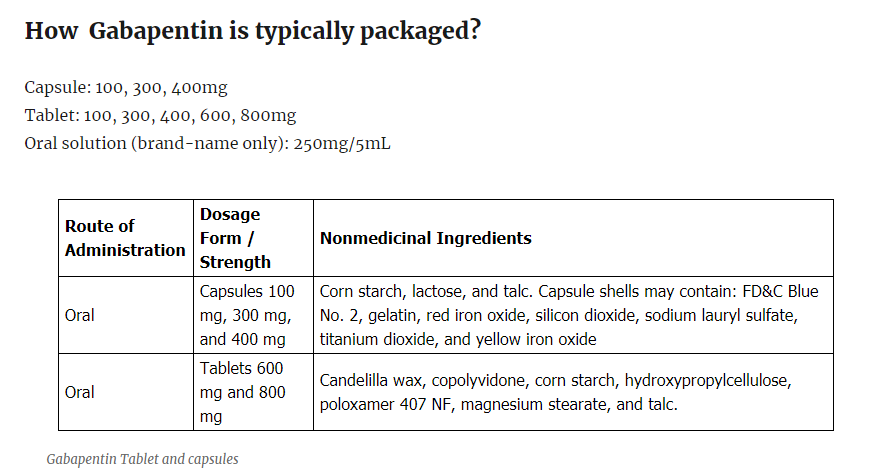
Gabapentin Dosing Considerations
Three gabapentin products are FDA approved to treat PHN. The different formulations cannot be interchanged and each has its own dosing schedule.
-
- For immediate-release gabapentin (Neurontin), dosing may be initiated with 300 mg on day 1, doubled on day 2 (300 mg twice a day), and tripled on day 3 (300 mg 3 times a day). The dose can then be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a maximum dose of 1,800 mg daily (divided into 3 daily doses). Clinical studies referenced in the package insert state that efficacy for a range of doses from 1,800 mg/day to 3,600 mg/day were observed; however, there was no additional benefit seen with doses greater than 1,800 mg/d.
- Gralise is an extended-release gabapentin formulation that also is FDA approved for PHN with a titration schedule that begins with 300 mg on day 1; 600 mg on day 2; 900 mg on days 3 to 6; 1,200 mg on days 7 to 10; 1,500 mg on days 11 to 14; and 1,800 mg on day 15 and thereafter.
- The third gabapentin formulation for PHN treatment is another extended-release product, Horizant. The starting dose is 600 mg in the morning for 3 days, increased to 600 mg twice daily on day 4 and thereafter. A daily dose of Horizant greater than 1,200 mg provided no additional benefit at the expense of side effects.
Several studies have evaluated off-label use of gabapentin in the treatment of other neuropathic pain conditions. A randomized, double-blind trial compared gabapentin to placebo in 135 patients with DPN over 8 weeks. The results showed a statistical benefit of gabapentin compared to placebo, at all end points, for pain improvement.
The gabapentin dosing regimen used in this study was 900 mg/d for week 1; 1,800 mg/d for week 2; 2,400 mg/d for week 3; and 3,600 mg/d for week 4. All the patients were titrated up to a dose of 3,600 mg/d, regardless of efficacy at lower doses. Patients who could not tolerate this dose were titrated down to the greatest tolerable dose.

Of the 84 patients randomized to the gabapentin group, 56 (67%) were able to tolerate 3,600 mg/d. During the first week, gabapentin resulted in improvement in sleep interference compared to placebo.
By the second week, gabapentin resulted in improvement in all pain rating scales compared to placebo. Of the 84 patients in the gabapentin group, 70 completed the study, and 7 patients withdrew due to adverse drug events (ADEs). Most ADEs reported in the gabapentin group were of mild or moderate intensity, and the most frequently reported effects were dizziness (23.8%), somnolence (22.6%), headache (10.7%), diarrhea (10.7%), confusion (8.3%), and nausea (8.3%).
A double-blind crossover study (n=40) assessed gabapentin for the treatment of DPN. The dose of gabapentin used in this trial was much lower, with patients titrated up every 3 days to a maximum dose of 900 mg/d. The end points evaluated in this study included level of pain on a visual analog pain scale (VAS), and scores on the present pain intensity scale, the McGill pain questionnaire (MPQ), and the global assessment of pain relief.
Statistical improvement between gabapentin and placebo was noted in only 1 end point, the MPQ score, with a mean reduction of 8.9 points for gabapentin compared to 2.2 points with placebo (P=0.03). No serious ADEs were noted, and the most common ADEs of gabapentin were drowsiness, fatigue, and imbalance. The results of this study suggest that gabapentin is not effective or is only minimally effective in treating painful DPN at a dose of 900 mg/d.5
A search in the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews was conducted to further examine dosing regimens for neuropathic pain. In a review analyzing 37 studies for gabapentin treatment in chronic neuropathic pain, the main outcome was Initiative on Methods, Measurement, and Pain Assessment in Clinical Trials (IMMPACT) definitions for moderate and substantial benefit in chronic pain studies.6 These were defined as follows:
- 30% reduction in pain over baseline (moderate)
- 50% reduction in pain over baseline (substantial)
- Much or very much improved on Patient Global Impression of Change (PGIC) (moderate)
- Very much improved on PGIC (substantial)
- Gabapentin was shown to be better than placebo across all studies for IMMPACT outcomes. The review concentrated on gabapentin doses of 1,200 mg/d or greater and reported that doses at or above this threshold were reasonably effective for treatment of various neuropathic pain types.
The upper threshold for maximum effective gabapentin doses ranged from 2,400 mg/d to 3,600 mg/d in the majority of studies reviewed.
ADEs and withdrawal rates for patients taking gabapentin doses of 1,200 mg/d or greater were compared to those for patients taking placebo in 20 studies with 4,125 participants. Common ADEs seen were somnolence, drowsiness, and sedation.
These occurred in 14% of participants in the gabapentin group versus 5% of those taking placebo. Data also showed gabapentin was associated with a higher incidence of dizziness (19% vs 5%), peripheral edema (7% vs 2.2%), and ataxia or gait disturbances (8.8% vs 1.1%).
The rate of serious events was similar between gabapentin and placebo groups. Twenty-two studies involving 4,448 patients reported on participant withdrawals due to ADEs, which occurred in 11% of patients taking gabapentin compared to 7.9% of those taking placebo.6
Postmarketing Abuse
Postmarketing reports have described symptoms of agitation, confusion, and disorientation upon abrupt withdrawal of gabapentin. Cases usually involve other potentiating factors, such as the use of higher than recommended doses for unapproved indications, a history of poly-substance abuse, or the use of gabapentin to relieve symptoms of withdrawal from other substances.1 In a study of postmortem toxicology, cases that tested positive for gabapentin or pregabalin were included to determine if abuse of these drugs contributed to the fatalities. Of the 13,766 cases investigated, 0.31% were positive for gabapentin. Of the gabapentin cases, 18.6% were considered abuse, and 4.7% were poisonings. An overwhelming majority of abuse cases (87.5%) also involved opioid intoxication, and 100% involved alcohol and/or opioids. In addition, a greater number of pregabalin cases were designated as abuse cases than gabapentin cases (48.1% vs 18.6%, respectively).7
Conclusion
Gabapentin has sufficient evidence showing its efficacy and safety in treating neuropathic pain. Effective treatment doses of gabapentin for neuropathic pain tend to be higher compared to effective treatment doses for other conditions. Gabapentin is a relatively safe medication. The most prevalent effects seen are drowsiness, somnolence, and sedation. It is necessary to start at lower doses of gabapentin and titrate up to a therapeutic dose. Ataxia and somnolence appear to exhibit a positive dose-response relationship; therefore, titrating the dose of gabapentin may help manage possible ADEs.