In a meta-analysis of trials evaluating the treatment of neuropathic pain, including painful polyneuropathy and spinal cord injury pain, gabapentin was shown to be safe and effective . Data from meta-analyses support the use of immediate-release gabapentin for reducing pain by more than 50% in diabetic neuropathy.
What is neuropathic pain?
Neuropathic pain can happen if your nervous system is damaged or not working correctly. You can feel pain from any of the various levels of the nervous system—the peripheral nerves, the spinal cord and the brain. Together, the spinal cord and the brain are known as the central nervous system. Peripheral nerves are the ones that are spread throughout the rest of your body to places likes organs, arms, legs, fingers and toes.
Damaged nerve fibers send the wrong signals to pain centers. Nerve function may change at the site of the nerve damage, as well as areas in the central nervous system (central sensitization).
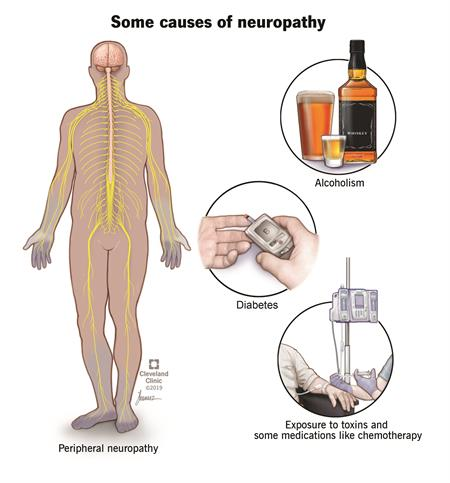
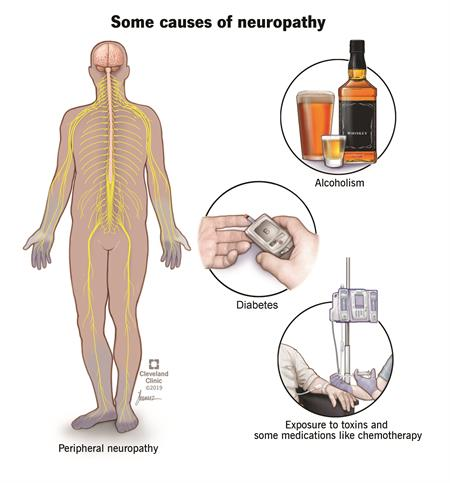
Neuropathy is a disturbance of function or a change in one or several nerves. Diabetes is responsible for about 30% of neuropathy cases. It is not always easy to tell the source of the neuropathic pain. There are hundreds of diseases that are linked to this kind of pain.
Data from a limited number of clinical trials support the use of extended-release gabapentin in reducing pain by more than 50% and improving sleep in diabetic neuropathy.
Based on guidelines from the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP), European Federation of Neurological Societies (EFNS), and Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM), gabapentin is effective and recommended for the management of peripheral neuropathy .
Based on guidelines from the EFNS, IASP, and National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE), gabapentin is effective and recommended as first-line therapy, supported by strong evidence, in the management of diabetic neuropathy.
The IASP guidelines recommend both immediate- and extended-release gabapentin . In contrast, a guideline from the American Academy of Neurology (AAN), American Association of Neuromuscular and Electrodiagnostic Medicine, and American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation states that gabapentin is probably effective and should be considered an alternative treatment for painful diabetic neuropathy based on limited benefit in 2 controlled trials.
Similarly, a position statement from the American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends gabapentin as a second-line option .