Gabapentin is an anti-epileptic drug, also called an anticonvulsant. It affects chemicals and nerves in the body that are involved in the cause of seizures and some types of pain.

Some inactive ingredients in the gabapentin tablets or capsules include:
-
-
- Lactose
- Talc
- Cornstarch
- Gelatin
- Colors such as FD&C blue no. 2, yellow iron oxide
- Titanium dioxide
- Poloxamer 407
- Magnesium stearate
- Copovidone, cornstarch
- Candelilla wax
- Hydroxypropyl cellulose
-
Dosing information
Usual Adult Dose for Epilepsy:
Initial dose: 300 mg orally on day one, 300 mg orally 2 times day on day two, then 300 mg orally 3 times a day on day three
Maintenance dose: 300 to 600 mg orally 3 times a day
Maximum dose: 3600 mg orally daily (in 3 divided doses)
-Maximum time between doses in the 3 times a day schedule should not exceed 12 hours
-The safety and effectiveness of gabapentin available under the trade name Gralise or Horizant in patients with epilepsy has not been studied.
Use: Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures, with and without secondary generalization
Usual Adult Dose for Postherpetic Neuralgia:
-Initial dose: 300 mg orally on day one, 300 mg orally 2 times day on day two, then 300 mg orally 3 times a day on day three
-Titrate up as needed for pain relief
-Maximum dose: 1800 mg per day (600 mg orally 3 times a day)
Gabapentin available under the trade name Gralise:
-Maintenance dose: Gralise should be titrated to 1800 mg orally once daily with the evening meal.
-Recommended titration schedule:
Day 1: 300 mg orally with the evening meal
Day 2: 600 mg orally with the evening meal
Days 3 through 6: 900 mg orally with the evening meal
Days 7 through 10: 1200 mg orally with the evening meal
Days 11 through 14: 1500 mg orally with the evening meal
Day 15: 1800 mg orally with the evening meal
COMMENT:
-Gralise is not interchangeable with other gabapentin products because of differing pharmacokinetic profiles that affect the frequency of administration.
Gabapentin enacarbil extended release tablets are available under the trade name Horizant:
-The recommended dosage is 600 mg orally 2 times a day. Therapy should be initiated at a dose of 600 mg orally in the morning for 3 days of therapy, then increased to 600 mg 2 times a day (1200 mg/day) on day four.
COMMENT:
Gabapentin enacarbil extended release tablets available under the trade name Horizant and gabapentin are not interchangeable.
Use: Postherpetic neuralgia
Usual Adult Dose for Restless Legs Syndrome:
Gabapentin enacarbil available under the trade name Horizant:
600 mg orally once daily with food at about 5 PM
Use: For the treatment of moderate-to-severe primary Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS) in adults
Usual Pediatric Dose for Epilepsy:
Less than 3 years: Not recommended
Greater than or equal to 3 and less than 12 years:
Starting Dose: Ranges from 10 to 15 mg/kg/day in 3 divided doses
Effective Dose: Reached by upward titration over a period of approximately 3 days; the effective dose in patients 5 years of age and older is 25 to 35 mg/kg/day in divided doses (3 times a day).
The effective dose in pediatric patients ages 3 and 4 years is 40 mg/kg/day and given in divided doses (3 times a day). Gabapentin may be administered as the oral solution, capsule, or tablet, or using combinations of these formulations. Dosages up to 50 mg/kg/day have been well tolerated in a long term clinical study. The maximum time interval between doses should not exceed 12 hours.
Greater than 12 years:
-Initial dose: 300 mg orally on day one, 300 mg orally 2 times a day on day two, then 300 mg orally 3 times a day on day three
-Maintenance dose: 900 to 1800 mg orally in 3 divided doses; the dose may be increased up to 1800 mg/day. Dosages up to 2400 mg/day have been well tolerated in long term clinical studies. Doses of 3600 mg/day have also been administered to a small number of patients for a relatively short duration, and have been well tolerated. The maximum time between doses in the three times a day schedule should not exceed 12 hours.
Use: Adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures, with and without secondary generalization in patients 3 years of age and older
Gabapentin is used together with other medicines to treat partial seizures in adults and children at least 3 years old.
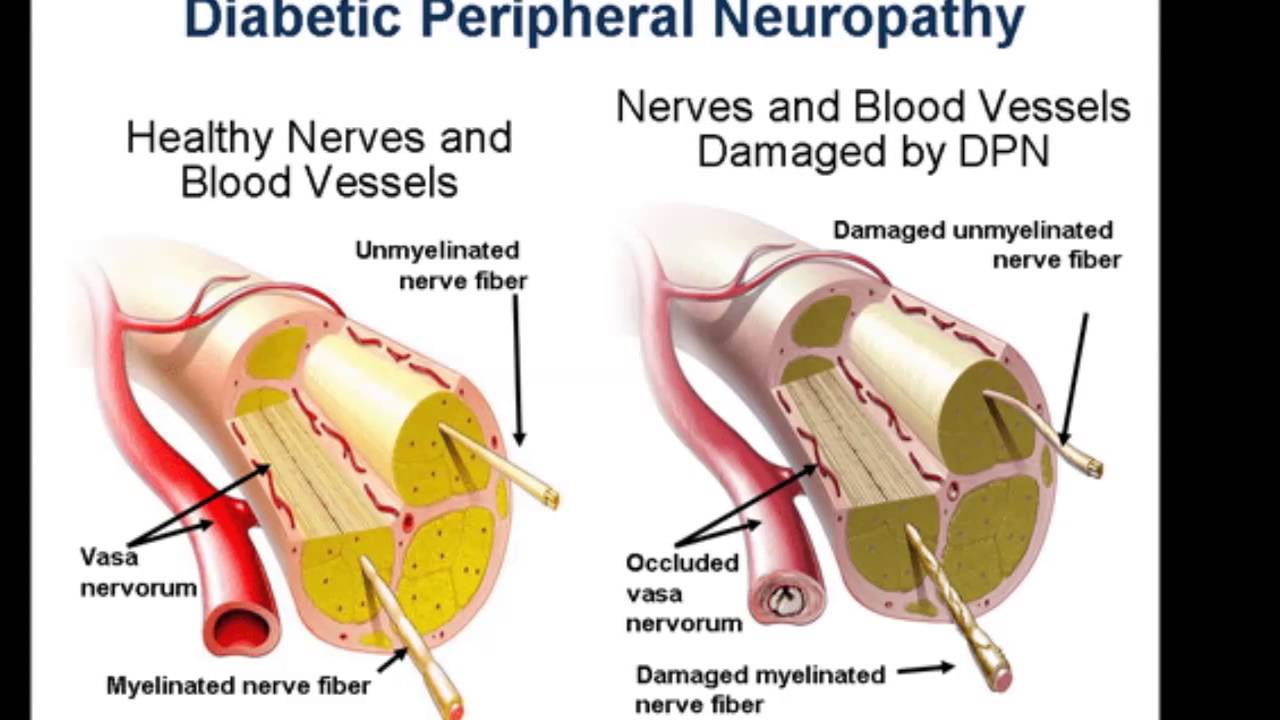
Gabapentin is also used to treat neuropathic pain (nerve pain) caused by herpes virus or shingles (herpes zoster) in adults.
Use only the brand and form of gabapentin your doctor has prescribed. Check your medicine each time you get a refill to make sure you receive the correct form.
The Gralise brand of gabapentin is indicated for the management of neuropathic pain only. It is not used for epilepsy.
Horizant is used to treat nerve pain and restless legs syndrome (RLS).
The Neurontin brand is used to treat seizures in adults and children who are at least 3 years old, in addition to neuropathic pain.
Gabapentin is part of its own drug class, called gabapentinoids. Typical dosages range from 100 milligrams to 800 milligrams of the drug.