What Is Gabapentin?
Gabapentin is a pharmaceutical medication originally intended for use in the treatment of seizures.
However, gabapentin is most commonly prescribed for conditions other than seizures and epilepsy, such as pain syndromes. Since gabapentin is not an opioid, in theory, it has lower abuse potential and is more readily prescribed for pain than more addictive medications. Gabapentin can also be used to treat:
-
-
- Nerve pain, such as from a shingles outbreak
- Treating alcohol or cocaine withdrawal
- Restless legs syndrome
- Diabetic neuropathy
- Fibromyalgia
- Hot flashes
-
How Does Gabapentin Work?
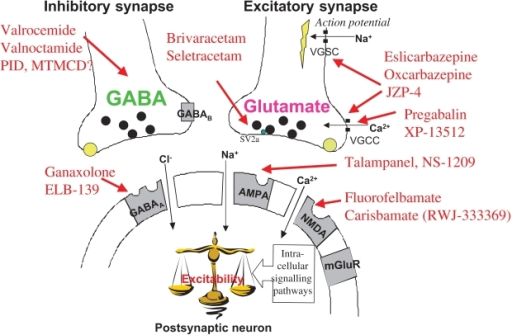
Gabapentin is a calming chemical that has a similar chemical structure to Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which is a brain chemical that calms the nervous system. However, gabapentin does not bind to the body’s GABA receptors. Instead, gabapentin affects the body’s calcium channels to reduce seizures and nerve pain.
How Addictive is Gabapentin?
Gabapentin is thought to be less addictive than opioid medications for pain relief. Overall, gabapentin is not considered a highly addictive drug. Many cases of gabapentin abuse occur in people who already have addictions to opioids and other drugs.
In response to increased abuse of gabapentin, some states are classifying gabapentin as a Schedule V controlled substance. While gabapentin appears to have low abuse potential, it is often used in conjunction with other, more addictive, drugs.
It’s possible to fatally overdose on gabapentin. Reports of gabapentin being abused alone, and with opioids, prompted the FDA to release a warning statement (in December 2019) about the fatal risk of respiratory depression. Signs of overdose include:
-
-
- Ataxia (decreased muscle coordination)
- Diarrhea
- Drooping eyelid
- Drowsiness and lethargy
- Double vision
- Excitation
- Hypoactivity
- Labored breathing
- Marked sedation
- Slurred speech
-
If you suspect an overdose, you need immediate medical treatment. The only way to remove the drug is through kidney dialysis in the emergency room.
Gabapentin Addiction Statistics
A study published in 2013 conducted in Kentucky showed that among 503 participants reporting illegal drug use, 15% reported using gabapentin to “get high” in the previous six months.
That percentage was a 165% increase from the year prior. A national assessment found that nearly a quarter of patients with co-prescriptions of opioids and gabapentin had three or more prescriptions exceeding established dosage thresholds.
In comparison, in patients prescribed just opioids or just gabapentin, the figures were 8% and 3% respectively.
Can You Overdose on Gabapentin?
Despite the well-known withdrawal side effects, it’s difficult to overdose on gabapentin. Studies have shown that even at very high levels of ingestion, people have only suffered mild to moderate physical and mental side effects that are rarely life-threatening. So far, there have been only two peer-reviewed case reports of death from gabapentin toxicity (related to gabapentin overdose). Despite this low statistic, gabapentin abuse as a suicide attempt has risen over the years.
While this means gabapentin is a relatively safe drug, it still should not be ingested in large amounts. However, people taking gabapentin should be aware that it does have particularly unpleasant withdrawal symptoms, even after taking it for a relatively short amount of time and at low doses.
Symptoms of Gabapentin Overdose
Most side effects of a gabapentin overdose will be related to an overall deceleration of the body’s systems. Drowsiness, muscle weakness, lethargy and drooping eyelids can be expected. Other gabapentin overdose symptoms include diarrhea and sedation. These symptoms arise because gabapentin is formulated to slow down misfirings in the brain that cause seizures.
Those who use gabapentin should be aware that stopping gabapentin abruptly can actually increase the chance of experiencing seizure activity. Suddenly removing the anti-seizure effect can cause a rebound, raising the risk of seizures. Gabapentin is a powerful drug that must be tapered slowly to avoid some of its more severe withdrawal side effects.
Is Gabapentin Considered as Controlled Substance ?
Gabapentin is not currently a controlled substance at the federal level, but certain states have made gabapentin a controlled substance at the state level. This includes Kentucky, Michigan, Tennessee, Virginia and West Virginia.
Does Gabapentin have any warnings when taking the drug?
The FDA has issued several warnings for gabapentin. These include certain side effects like Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms, or DRESS, and allergic reactions like anaphylaxis or angioedema, a swelling of the lips or face. The drug should be stopped immediately if any of those side effects are suspected. Other side effects that need to be monitored include impaired motor skills, drowsiness, dizziness, mental status changes, slowed breathing and a possible increase in suicide risk.
How is Gabapentin taken?
Gabapentin is taken by mouth. There are various dosage forms of the medication, including capsules, oral solutions and tablets. The drug comes in both immediate-release (IR) and extended-release (ER) formulations.
![]()
Does Gabapentin have other names?
Gabapentin may be sold under different brand names, including Neurontin and Gralise.
What ingredients are in Gabapentin?
Gabapentin is part of its own drug class, called gabapentinoids. Typical dosages range from 100 milligrams to 800 milligrams of the drug. Some inactive ingredients in the gabapentin tablets or capsules include:
Gabapentin is not currently a controlled substance at the federal level, but certain states have made gabapentin a controlled substance at the state level. This includes Kentucky, Michigan, Tennessee, Virginia and West Virginia.
Does Gabapentin have any warnings when taking the drug?
The FDA has issued several warnings for gabapentin. These include certain side effects like Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms, or DRESS, and allergic reactions like anaphylaxis or angioedema, a swelling of the lips or face. The drug should be stopped immediately if any of those side effects are suspected.
Other side effects that need to be monitored include impaired motor skills, drowsiness, dizziness, mental status changes, slowed breathing and a possible increase in suicide risk.
How is Gabapentin taken?
Gabapentin is taken by mouth. There are various dosage forms of the medication, including capsules, oral solutions and tablets. The drug comes in both immediate-release (IR) and extended-release (ER) formulations.
Does Gabapentin have other names?
Gabapentin may be sold under different brand names, including Neurontin and Gralise.
What ingredients are in Gabapentin?
Gabapentin is part of its own drug class, called gabapentinoids. Typical dosages range from 100 milligrams to 800 milligrams of the drug. Some inactive ingredients in the gabapentin tablets or capsules include:
-
-
-
- Lactose
- Talc
- Cornstarch
- Gelatin
- Colors such as FD&C blue no. 2, yellow iron oxide
- Titanium dioxide
- Poloxamer 407
- Magnesium stearate
- Copovidone, cornstarch
- Candelilla wax
- Hydroxypropyl cellulose
-
-